The Theory of Perfect Pitch According to Harmonics
Perfect Pitch Training in the Harmonic Equalizer
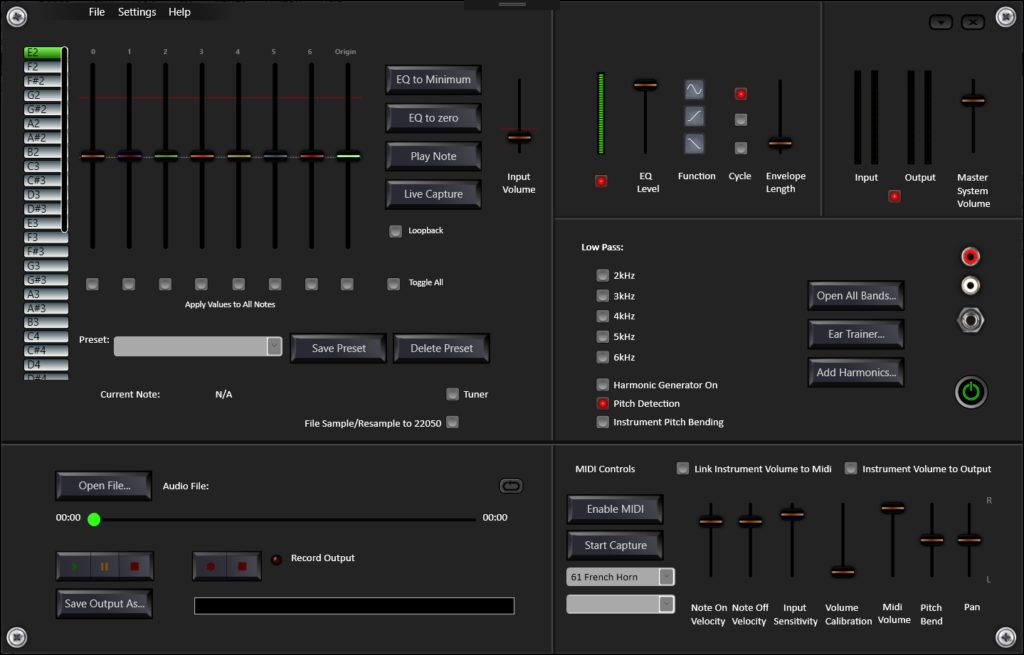
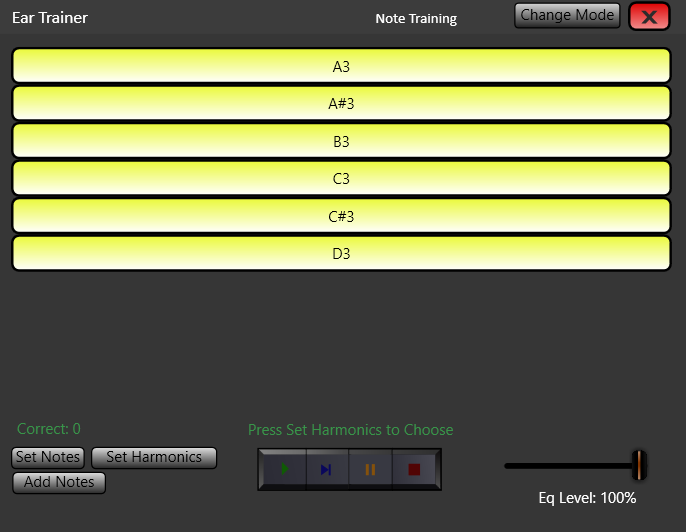
The Harmonic Equalizer is an exciting new Windows tool with many uses, including ear training. Firstly, consider the unique qualities of each musical note, apart from simply their fundamental pitch. The musician with perfect pitch hears each note by its own quality, which we could call a “timbre”. Typically, the timbre of a tonal sound comes from the relative levels of its harmonic frequencies (harmonic overtones). In the Harmonic Equalizer, the harmonic preset named, “Absolute Pitch” is a representation of the prominent harmonics thought to exist for the notes. The purpose of this preset is to exaggerate the perfect pitch qualities of each note (even in real time as you play your instrument).


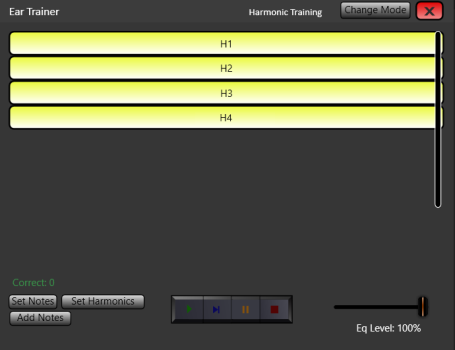
The possible reasons for these differences in timbre are discussed below but for now, let’s dive in and listen to some examples. The example below shows how the ear trainer works. Of course, the task to identify the note is easy as there are only two notes loaded in this example, but it shows how the example notes differ in sound. This is how you will develop your ear to listen and identify sounds by their harmonic characteristics. Listen to how much brighter the tone of the F# is, compared to D#. Both have strong 5th harmonics (4th overtone), but the D# has quite a prominent 3rd harmonic also, which affects the timbre of the note.
If you haven’t done so already, it’s now time to take the first step in your perfect pitch training! Go to your instrument now and play the two notes you have just been listening to (D#3 and F#3). Having been listening to the audio from the demo, you will find it easy to tune in to the featured harmonics (particularly the 5th). You may be surprised to hear how different these two notes sound from each other. You might even wonder why you never noticed this before!
Keep Training!…
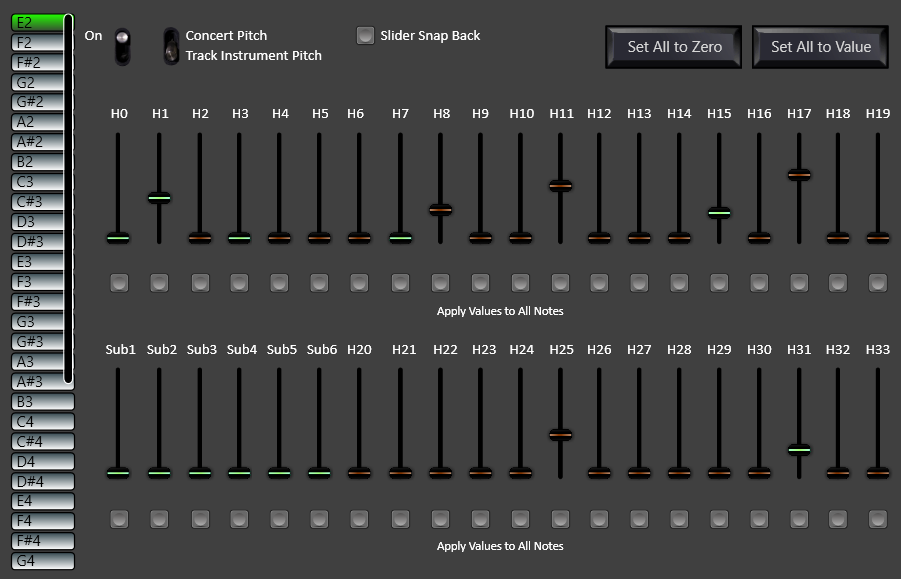
The Absolute Pitch Preset is a great tool but is only the beginning of what you can do with the Harmonic Equalizer. The ear training function can be set to Harmonic Training mode to let you improve these skills. For example, create your own preset where all the third harmonics are amplified then another preset with loud fourth harmonics, turn both on in harmonic training and learn to quickly pick out which harmonic is being amplified. Become more advanced by boosting combinations of more than one harmonic at the same time and train to identify combinations all the way up to the 33rd harmonic. These advanced skills are usually only possessed by elite musicians and music producers.


Real-Time Live Harmonic Processing
A great way to listen to absolute pitch harmonic sounds is to play an electric guitar or other instrument through the Harmonic Equalizer. The application will alter the sound in real-time so you can listen as you play. In fact, it will apply any preset you create to the notes you play by quickly identifying the note being played and applying your chosen harmonic profile for that note. Live capture can be set to use an ASIO driver if you wish, for very low latency. ASIO capture can also be routed to other applications using ASIO Link Pro so the Harmonic Equalizer can be used as part of a DAW setup or the signal can be sent to a VST Host.
Harmonics in Composition
How about experimenting with harmonic sounds in your compositions? As well as creating inspiring audio effects and atmosphere, you can set up harmonic profiles where prominent harmonics descend as your notes ascend, or vice versa, creating counterpoint between fundamental tones and harmonic tones. Play with those strange harmonics! Some harmonic overtones are not matched in frequency to any fundamental in equal temperament. Why not try incorporating these alien frequencies into your compositions. These frequencies do exist in the audio already, although previously in the background, and can sound beautiful as the Harmonic Equalizer brings them to your attention.
Get started now by downloading here!
If you wish to download from from Microsoft, you can do it here! The Harmonic Equalizer is a certified Windows App in the Windows Store.
More Functions of the Harmonic Equalizer….
File Player
As well as the button to play a sample note, there is a file player, which plays a chosen .wav or mp3 file through the live equalizer and detects the fundamental pitch of the audio as it plays. Or the pitch detection may be switched off so that you can choose which audio filters are applied to the audio. The file recorder on the player can be used to record any output at the computer audio out, so can record a live instrument session too.
Full Band EQ
A full band equalizer is also included in the application. The frequency bands used to isolate harmonics are very accurate and precise. The full band EQ presents all of these bands at once for use with file play or live capture.
MIDI
Using the fast note pitch detection, there is also a Voice to MIDI function. You can play or sing a note into the computer input then the Midi function will play that note on Midi. It can be used to send a signal to a midi output or it can be used with a Virtual Midi Synthesizer or it can send MIDI signals to a VST Host/DAW via LoopBe. Harmonics of the midi notes may be added in real time via the Harmonic Generator.
Harmonics – Definition
Every tonal sound from an instrument, voice, or any other source contains a fundamental frequency and harmonics (overtones). The harmonics of a tone are multiples of the fundamental frequency. When you play an A440 on your instrument, the sound you hear is made up from 440 Hz, 880 Hz, 1320 Hz, 1760 Hz, 2200 Hz, and so on.
Different instruments have different harmonic spectra. The following diagrams show the spectra for a clarinet and a guitar.
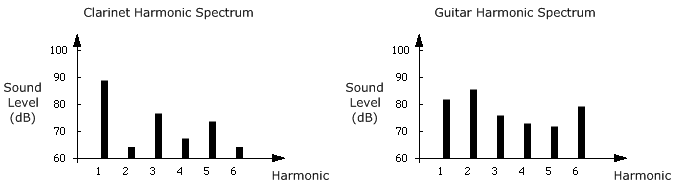
The harmonic spectra are different. The levels of the harmonics of tonal sound contribute to the timbre to the sound. We can easily tell the difference between a clarinet and a guitar because they have very different harmonic spectra.
Regarding perfect pitch, musicians who have perfect pitch hear differences in “quality”, or timbre, between the notes. However, the harmonic spectra is determined by the instrument.
The theory of perfect pitch according to harmonics is that differences in harmonic levels between different notes is only perceived by the listener. There is no physical difference in timbre between the different notes. The perceived difference between the notes is likely to be due to the frequency response and resonant frequencies of the human ear. Like a microphone, the human ear can hear some frequencies better than others and contains certain parts, which are able to resonate strongly at particular frequencies. Any tonal sound entering the ear involves a range of harmonic frequencies. The result is that we perceive some frequencies as much louder than others even if they have the same physical loudness.
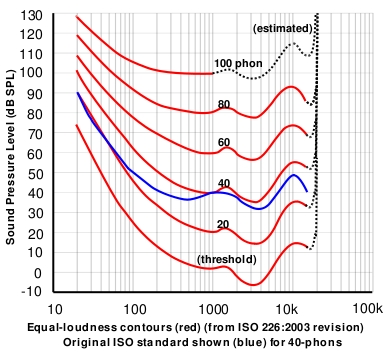
The above graph shows the equal loudness response for the human ear, which is much the same for all people. The bottom red line shows how loud the sound needed to be so that it could be heard by the test subjects. The sound at 20 Hz had to be played at over 70 dB SPL to be heard, while a sound of 1000 Hz could be heard at around 3 dB. The ear is most sensitive at 4000 Hz and a sound at 30 Hz has to be almost one million times as powerful as one at 4 kHz to be perceived the same.
The dips in the graph show the resonances of the ear, which are a result of the combination of resonating parts. For example, the auditory canal has a resonance at about 3 kHz. Other considerations are the vibration of the eardrum, the bones in the middle ear, and the complex behavior of the cochlea.
Of course, the equal loudness response of the ear is only part of the story of human hearing. There are many other phenomena going on when the ear is subjected to multiple frequencies. For example, the extent to which one frequency is masked by another depends greatly on the pitch of these frequencies.
In conclusion, perfect pitch timbres exist due to perceived spectra of the harmonics of the notes. On the one hand, there is the physical harmonic spectrum of a tonal sound. On the other, there is an internal spectrum from the response of the ear. It is thought that those who have perfect pitch are able to distinguish the spectrum of the sound resulting from the resonances of the ear from the physical spectrum created by the instrument. The main reason that perfect pitch is so rare could be that we tend to fixate on the fundamental pitch of the notes and, as musicians, the harmonics are not regarded with much importance. To hear with perfect pitch, you need to be able to listen to the harmonics.
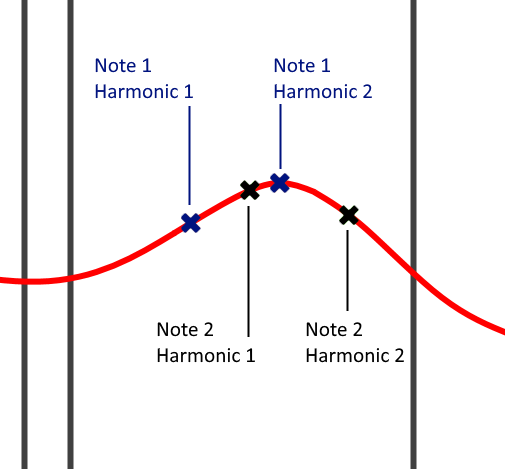
For the sake of example, imagine a scenario shown above. Note 1 has Harmonic 2 above Harmonic 1 on the curve, while Note 2 has Harmonic 2 below Harmonic 1 on the curve. This means the relative perceived levels of the harmonics will differ between the two notes. It is likely (although not proven) that the perfect pitch timbres are a result of the resonances of the ear. However, it is also worth considering that the harmonic range of the harmonics of a given note could give rise to perfect pitch, even without the resonances. Simply being able to appreciate the multiple frequencies within any tonal sound and the gaps between those frequencies (gaps between harmonics) may give more information to the brain to be used for the memory or identification of that tonal sound (note). For the brain to memorize just one single frequency may be impossible, but the fundamental plus harmonics may create a map of information, which the brain is able to store. Of course, it will be interesting in future to see more research in this area.
Harmonic Ear Training
The Harmonic Equalizer has an Ear Training Function to train your recognition of harmonics and harmonic combinations. Simply select the notes you wish to play and the harmonic presets (for example, 1st Harmonics, 2nd Harmonics, or any preset you have created yourself). The Ear Trainer will then play your notes at random and allow you to practice identifying which harmonic is being amplified. The mix between the original signal and the selected harmonics can be adjusted.
Perfect Pitch Training
The harmonic preset named, “Absolute Pitch” is a representation of the prominent harmonics thought to exist for the notes, according to the theory outlined above. The purpose of this preset is to amplify the perfect pitch experience. The Ear Trainer can be used in the same way as Harmonic Ear Training except the task is to identify the note playing, as the perfect pitch quality of each note is exaggerated as it plays.
To get started learning perfect pitch now – download the Harmonic Equalizer here. There is no subscription for the software, only a single one-off low payment! To learn about the many other functions of the Harmonic Equalizer, keep reading…

The Harmonic Equalizer is a 7-band EQ to match the fundamental and first six harmonics of the fundamental frequency at the input. There is also a 40-band harmonic generator, which can add harmonic frequencies, including 6 sub-harmonics. This means you can play notes and melodies in real time and hear whichever harmonics you choose, up to the 33rd harmonic. You can choose to amplify or suppress the same harmonics for all the notes you play or you can select different ones. You can pick multiple harmonics or narrow down to just one.
Play your electric guitar or other instrument through the Harmonic EQ and see what sounds you can create! There are many presets already available to set the levels for all the notes. These are based on the various effects and uses for the sounds. For example, play melodies using harmonics, create melodies from harmonics of different notes that are close to one another, create counterpoint between note fundamentals and harmonics. You can set your levels so that a descending note melody creates a simultaneous ascending harmonic melody. Create other-worldly sounds! Some harmonics are not exactly equivalent to any note on the equal temperament scale but we can still use them together with the conventional scale and unlock new melodies using these harmonic frequencies.
The Harmonic Equalizer as a VST
The current version of the application can be used with a DAW or VST Host by routing via ASIO Link Pro. Also, MIDI signals can be sent to a VST Host. However, the full integration of the Harmonic Equalizer as a VST Plugin is being considered for upcoming versions. Any purchase of the application includes all future updates.
Start Using Harmonics Now!….